Review paper on how to recover Node failure using (Multi-Protocol Label Switching (MPLS) Network and enhance the energy of signal
Nisha 1, Dr. Rashid Hussain 2 Ph.D. Scholar 1, Associate Professor 2
Suresh GyanVihar University, Mahal Jagatpura, Jaipur 1, 2
Abstract: Multi-Protocol Label Switching is a traffic routing mechanism in which (MPLS-FRR) MPLS fast reroute mechanism deviate the traffic in case of networks failure. The MPLS used this application of fast reroute in case failure of network. The main aim of fast reroute is that packet is reroute from the intermediate point at which data has been lost. With the help of identifying the failure node in MPLS, alternate path has been established to push packets from source to destination node. The process in which label switch path (LSP) has calculated before network failure is called fast reroute. With the help of error recovery technique in MPLS, the network become error tolerant and energy of network can be enhanced by using the fast reroute technique.
Keyword: Multi-Protocol Label Switching, MPLS FRR, Network life time, error recovery.
- Introduction
MPLS(Multi protocol label switching) has become one of the most network backbone technology. This technology
helps to deliver highly scalable, end to end IP service, authenticate data to the destination. In case of error in path, MPLS first establish the label switched path (LSP) and then forward the packet to new established node. Due to this MPLS shows slow recovery of path with LSP.
First of all fast reroute mechanism over MPLS network has been established and then find the problem of packet loss and delay in network because of link failure. Now MPLS has established new label switched path and forward to the packet to new path of LSP. With the help of fast reroute process, packet disorder has been avoid and packet delivery time has been decreased.
In this paper, We have established the new algorithm for MPLS network that belongs to faulty node and reroute the path by using simulator. Error recovery time is most important for fault tolerance. So algorithm may help to achieve the recovery time. Since there is packet loss, time delay and acknowledgement, traffic in the rerouting path will definitely be increased. Which is not preferable [10]. By network failure, we mean error occurs in label switch path and then proposed algorithm switches the traffic to fast reroute path.
So we propose a mechanism for error Recovery in an LSP. This unites the path protection local repair and global repair methods. By protecting the data to be failure, it also provides significant reduction of delay with the fast reroute after the link failure as the recovery technique has taken nearest to the failure point of data.
The first aim of this paper is to find route protection in MPLS network. And the path is calculated on the basis of labels. The second goal is to find the fault in path and then traffic is resend from the proposed algorithm.
- BACKGROUND AND RELATED WORK
In this section, MPLS-FRR has been explained in basic terminology for improving the internet behavior in speed. For each packet, forwarding and routing operation has been setup according to the destination node address in packet header. According to routing algorithm, each node establish next hop based on routing table.
The network has two or more path that sends data from ingress node to egress node. These path are called by primary path and secondary or alternative path. Alternative path is that at which we send date when there is failure in data along primary path. The alternative path can be set along with primary path or after failure of primary path.. Different methodhave been applied for time minimization and error recovery. Alternative path selection should be based on local or global repair.The ingress node should be able to detect the fault node and reroute to the alternative algorithm.
There are number of techniques and algorithm in which fault recovery, some are related to domain of link failure recovery and some are based on tunnel recovery. These techniques are tested to recover packet loss, recovery time. The major type of recovery scheme is used by MPLS is error recovery and rerouting is defined under figure 1 which shows the MPLS based network.
To strengthen IP network MPLS is scalable broadband technique. In MPLS network, packet enters through ingress node and label are assigned to these packets for the transmission. To forward packet short fixed length label is assigned.
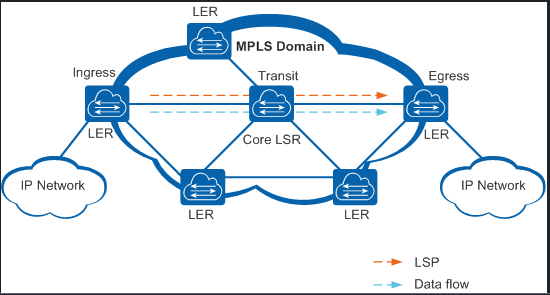
Fig.1 This diagram illustrates how a simple MPLS network works
Label switched path (LSP) forward the packets which are assigned by label switch router (LSR) that makes the decision to forward the packet based on the label contents. For the failure of network and to work quickly to recover path fast reroute (FRR) technology has been used. These are local mechanism that enable the failure-detecting router to switch packets to reconfigure backup LSP [13]. At each hop, LSR removes each existing label and applies the label which tells that how to forward to the next hop. Labels are removed at the last router in the LSP. And the last router is called egress router. As faults occur in IP network in the same way error occur in the MPLS network. For resolving these error a specific technique should be used.
III. PROBLEM DEFINITION
- Problem Definition
Because of node failure due to primary label switch path (LSP) failure, the data needs to be rerouted across the secondary path that is alternative path of LSP. Which is equivalent to carry data over the new LSP. So in order to reduce the LSP switchover time, a new LSP has to be established before occurrence of the fault over the network. The earlier used approach has a very slow response and the latter approached used has much better response than earlier one.
a.One- to-One back up path
This path is used for tiny network. It does not provide result for number of path network. So not a good technology to send data.
b.Multiple-to-one backup
For this ingress node and transmission nodes is to be setup. Since routing for every single node has to be done so it will take a lot of time. Ingress node takes less time but other transmission nodes take high time to transmit.
c.Single/ dual node failure
When dual node is fails due to transmission there is increase in transmission time, it is efficient technique only for transmission of single node.
- METHODOLOGY& ALGORITHM
In our proposed work, When there is a error across LSR, packets are sent back with the help of backward LSP. When all packets are sent back to starting node that is ingress node and it has been rerouted to the alternative path provided be LSP. And the time period has increased which was used to send the data from the ingress node. The packets which are stored to ingress nodes are send to the alternative nodes and with this global ordering of packets has been maintained during the whole process.
In MPLS network, ingress nodes have assigned packets to select the label switch path (LSP). In this LSP any failure occurs to take MPLS fast reroute to find an alternative path [13].
Local repair means after identifying the failure in the link, we have to find a neighbor node through which packets can be sent [14]. And for rerouting there will be increase in transmission of time. Figure 2 shows an example of local repair technique.
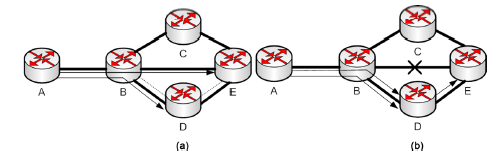
Figure 2 Switching to the bypass tunnel in case of failure of the communication channel.
PROPOSED FAULT RECOVERY PROTOCOL
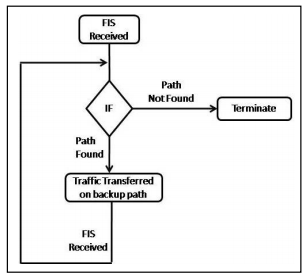
Figure 3 PROPOSED ALGORITHM
ALGORITHM
Protocol running on Ingress LSR,
- upon reception of FIS
- If path not found against failure Link then
- Terminate algorithm
- Else
- Switch traffic to backup path
- If FIS received through backup path then
- Switch traffic to second backup path
- If original working path restored
- Switch traffic to it
- CONCLUSIONS
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) develops a favorable technique to enhance the efficiency of a network by using error recovery technology and energy of a network is also enhanced by using our proposed technology. Number of technology for decreasing time to reroute has been used to modify our need and then proposed technology shows the better result.
REFERENCES
- Kini, S. Ramasubramanian, A. Kvalbein, and A. Hansen, “Fast recovery from dual link failures in ip networks,” in Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM, 2009, pp. 1368–1376.
- Mailland, J., & Driscoll, K. (2017). The French connection machine. IEEE Spectrum, 54(7), 32-37.
- Robertazzi, T. G. (2017). Multiprotocol label switching (MPLS). In Introduction to Computer Networking(pp. 61-65). Springer, Cham.
- https://digitalrevolver.com/switching-evolution/
- Shu, Z., Wan, J., Lin, J., Wang, S., Li, D., Rho, S., & Yang, C. (2016). Traffic engineering in software-defined networking: Measurement and management. IEEE access, 4, 3246-3256.
- Johnson, D., Hu, Y. C., &Maltz, D. (2007). The dynamic source routing protocol (DSR) for mobile ad hoc networks for IPv4(Vol. 260). RFC 4728.
- Huitema, C. (1998). IPv6: the new Internet protocol(p. 2). Prentice Hall PTR.
- Cole, R., Shur, D., &Villamizar, C. (1996). IP over ATM: A framework document. RFC1932, April.
- Suzuki, T. (1994). ATM adaptation layer protocol. IEEE Communications Magazine, 32(4), 80-83.
- DongmeiWang ;Guangzhi Li Networking, IEEE/ACM Transactions on,” Efficient Distributed Bandwidth Management for MPLS Fast Reroute” Volume: 16 , Issue: 2 ,2008
- Smith, D., Mullooly, J., Jaeger, W., & Scholl, T. (2011). Label Edge Router Forwarding of IPv4 Option Packets. In RFC 6178 (Proposed Standard). Internet Engineering Task Force.
- https://support.huawei.com/enterprise/tr/doc/EDOC1000166638/7c5ca4fb/basic-mpls-architecture#fig_dc_fd_mpls_000401
- Rosen, E., et al. ”Multiprotocol Label Switching Architecture”, Internet draft< draft-ietf-mpls-arch- 05.txt>, April 1999.
- ShrinivasaKini, Srinivasan Ramasubramanian, Amund Kvalbein, Audun F. Hansen,” Fast Recovery from Dual Link or Single Node Failures in IP Networks Using Tunneling “
